串口通信
串口(Serial)作为 MCU 常用的通信外设,应用非常广泛,如日志打印、通信交互、控制等。通常我们使用异步串口(UART)接口通信,通常只有 RX,TX两根线即可完成接收和发送的功能。
串口通信的底层逻辑非常容易理解,就像是我们日常两人谈话或多人谈话交流一样,我们想要表达一些意思时,需要一个字一个字念出来,在场的所有人都能听到,同时如果有其他人同时说话,可能接听者就容易误解。同时,不同的人说话速度、连读可能不一样,因此为了提高交流效率,要求大家都用同样的语速和语言交流。
对于串口外设来说,有以下参数必须需要设置:
- 波特率
- 位数
- 停止位
- 校验位
通信双方必须配置一致才能正常通信。
由于计算机的发展,现在常用的笔记本电脑或台式机已经不再附带串口,但可使用USB转串口工具来使用串口设备。在本开发板中自带一个USB转串口的电路,电脑使用 Type-C 线连接即可使用串口功能。本开发板的串口的电路如下:
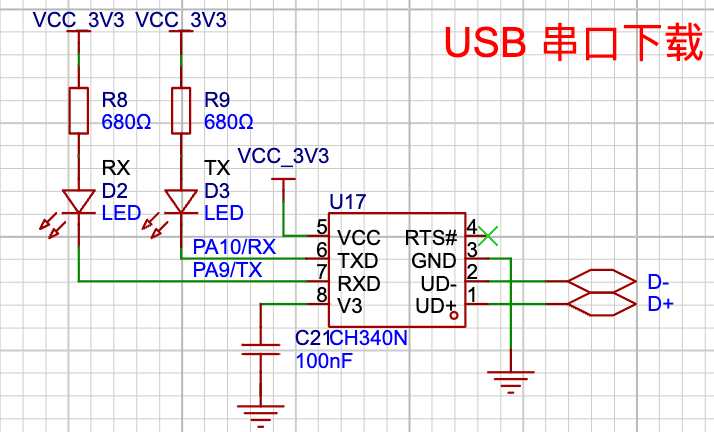
该电路可用于串口下载程序,也可在单片机程序中作为串口与电脑进行通信。
示例: examples/uart.rs
#![no_std] #![no_main] use embedded_io::Write; use hal::usart::AnyUsart; use heapless::String; use py32f030_hal as hal; use {defmt_rtt as _, panic_probe as _}; #[cortex_m_rt::entry] fn main() -> ! { let p = hal::init(Default::default()); let gpioa = p.GPIOA.split(); let tx = gpioa.PA9; let rx = gpioa.PA10; let usart = AnyUsart::new(p.USART1, Some(rx), Some(tx), None, None, Default::default()); let (_, mut tx) = usart.split(); defmt::info!("usart start..."); let buf: String<20> = "hello rust\r\n".into(); loop { // 使用标准接口来发送串口数据 let _ = write!(tx, "example for usart\r\n"); // 使用自定义的驱动接口发送串口数据 let _ = tx.write(buf.as_bytes()); defmt::info!("send: {} ", buf.as_bytes()); cortex_m::asm::delay(1000 * 1000 * 10); } }
测试如下
➜ py32f030-hal git:(main) ✗ cargo r --example uart
warning: unused manifest key: dependencies.embedded-io-async.option
Finished `dev` profile [optimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.03s
Running `probe-rs run --chip PY32F030x8 target/thumbv6m-none-eabi/debug/examples/uart`
Erasing ✔ [00:00:00] [########################################################################] 12.00 KiB/12.00 KiB @ 84.02 KiB/s (eta 0s )
Programming ✔ [00:00:02] [#########################################################################] 11.25 KiB/11.25 KiB @ 3.91 KiB/s (eta 0s ) Finished in 3.062s
INFO usart start...
└─ uart::__cortex_m_rt_main @ examples/uart.rs:23
INFO send: [104, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 114, 117, 115, 116, 13, 10]
└─ uart::__cortex_m_rt_main @ examples/uart.rs:32
INFO send: [104, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 114, 117, 115, 116, 13, 10]
└─ uart::__cortex_m_rt_main @ examples/uart.rs:32
INFO send: [104, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 114, 117, 115, 116, 13, 10]
└─ uart::__cortex_m_rt_main @ examples/uart.rs:32
INFO send: [104, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 114, 117, 115, 116, 13, 10]
└─ uart::__cortex_m_rt_main @ examples/uart.rs:32
INFO send: [104, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 114, 117, 115, 116, 13, 10]
└─ uart::__cortex_m_rt_main @ examples/uart.rs:32
^C%
电脑主机端需要串口工具用于显示单片机发送的信息。如果没有安装串口工具,可以参考 串口工具
在测试代码的串口配置中,使用了驱动默认的配置,Default::default(),在Vscode 点击代码可以进入驱动层看到如下:
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { /// 串口的综合配置结构体 #[derive(Default)] pub struct Config { pub baud_rate: BaudRate, pub stop_bit: StopBits, pub word_len: WordLen, pub parity: Parity, // pub hw_flow_ctrl: HwFlowCtrl, pub data_bits: DataBits, pub over_sampling: OverSampling, // pub mode: T, } /// 串口的波特率定义 #[derive(Default)] pub enum BaudRate { // Auto = 0, Bps300 = 300, Bps1200 = 1200, Bps2400 = 2400, Bps4800 = 4800, Bps9600 = 9600, Bps1440 = 1440, Bps19200 = 19200, Bps28800 = 28800, Bps38400 = 38400, Bps57600 = 57600, Bps74880 = 74880, #[default] Bps115200 = 115200, Bps230400 = 230400, } /// 串口数据长度 #[derive(Default)] pub enum WordLen { #[default] WordLen8 = 0, WordLen9 = 1, } ... }
在各个配置中,使用宏#[derive(Default)] 声明使用各个定义默认枚举所标记的值。
其他示例:examples/embassy_uart.rs
以下展示使用异步接口来与主机端通信,展示接收和发送数据。以下代码也可轻松改造成接收和发送使用不同的任务去运行。
#![no_std] #![no_main] // use embedded_io::Write; use defmt::Debug2Format; use hal::usart::AnyUsart; use heapless::String; use py32f030_hal::{self as hal, mode::Async}; use {defmt_rtt as _, panic_probe as _}; use embassy_executor::Spawner; use embassy_time::Timer; #[embassy_executor::main] async fn main(_spawner: Spawner) { let p = hal::init(Default::default()); let gpioa = p.GPIOA.split(); let rx = gpioa.PA10; let tx = gpioa.PA9; let usart: AnyUsart<_, Async> = AnyUsart::new(p.USART1, Some(rx), Some(tx), None, None, Default::default()); let (mut rx, mut tx) = usart.split(); defmt::info!("usart start..."); let buf: String<20> = "hello rust\r\n".into(); let mut rx_buf: [u8; 10] = [0; 10]; loop { // 使用标准接口来发送串口数据 // let _ = write!(tx, "example for usart\r\n"); let rst = rx.read(&mut rx_buf).await; // let rst = rx.read_with_idle(&mut rx_buf).await; // defmt::info!("recv: rst: {:?} {:x}", Debug2Format(&rst), rx_buf); // 使用自定义的驱动接口发送串口数据 let rst = tx.write(buf.as_bytes()).await; defmt::info!("send: rst:{} {:x} ", Debug2Format(&rst), buf.as_bytes()); Timer::after_secs(1).await; } }
运行:cargo r --example embassy_uart --features embassy